
Green, Social and Sustainability Bonds Q&A Part One: Digging into details on green bonds
Sustainable bonds (the collective term for green, social and sustainability bonds) is a growing asset class that has become a by-word for impact investing in a fixed income portfolio. As interest in this asset class continues to increase, so does the need for understanding the nuances behind them.
Here we share a few of the questions we are being asked about green bonds:
1. Do green bonds do more than just combat carbon emissions?
It could be assumed that green bonds are just a tool to help corporates and governments achieve their net zero carbon emissions targets. However, green bonds are used for a much broader range of environmental challenges. We see the global green bonds universe as being divided into four main themes: smart buildings, low carbon transport, sustainable ecosystems and smart energy infrastructure.
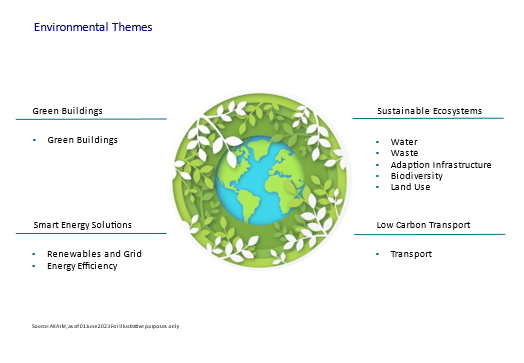
None of these themes work in silo and all can have a role towards lowering carbon emissions but, as the themes demonstrate, green bonds should be seen as part of the route to a sustainable economy beyond carbon emissions. Looking at the sub-themes within sustainable ecosystems demonstrates these separate priorities as well as the link to our carbon footprint:
Water
Water quality and quantity is a universal concern and one that impacts all individuals regardless of where they are living. Water stress – the combination of quality, quantity and access – is a focus for United Nations Sustainable Development Goals and one that companies from at-risk sectors such as agriculture to textiles can do more to address. While water stress may not be directly linked to a low carbon economy, the excessive use of it in some sectors and unchecked pollution controversies has an impact on the ecosystem and, therefore, how successfully carbon can be neutralised.
Waste
From food to electronics, the world’s growing population is putting pressure on natural resources by increasing demand for aspects such as energy, food and water. E-waste, for example, is one of the fastest growing waste streams in the EU and less than 40% is currently recycled
2. How do green bonds provide a positive impact for biodiversity?
Biodiversity loss is being addressed through green bonds. While still a new conversation, the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) agreed in December 2022 during COP 15 has helped highlight the urgent need to protect nature. As companies realise the negative impact that biodiversity loss can have on their operations, green bonds are one solution for achieving a more nature-positive outcome. For example, we can think of New Zealand’s green bonds that are intended to advance the country's progress towards low carbon development, concretized in their recently reinforced Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), as well as the preservation of biodiversity: in 2020 the government published a biodiversity strategy setting a 30-year strategic direction which is supported by 5-year implementation plans, the last of which was released in April 2022. More specifically, it focuses on:
Living and Natural Resources and Land Use: sustainable agriculture, forestry, land restoration and nature-based solutions. This is of particular relevance as livestock farming accounts for c. 50% of gross greenhouse gas emissions
Terrestrial and Aquatic Biodiversity: protection of freshwater ecosystems, restoration of the natural environment including indigenous flora, and protection of marine species.
Investors are also increasingly aware of the need to engage with companies on the topic of biodiversity as the potential risks to their portfolios becomes more apparent. The GBF’s targets help with this conversation by providing guidance on a direction of travel for countries and companies. It is likely that companies will need to disclose more with regards to their biodiversity footprint especially as corporates embrace the GBF’s target of standardising accounting and reporting.
However, the lack of good quality data is a stumbling block: it tends to be location specific, difficult to compare and takes time for the research to come through and provide useful data. Nevertheless, with more regulation, we have seen a catalyst for positive development in data provision.
3. How to navigate volatile markets with green bonds?
While green bonds often only sit in a responsible investing bucket for investors, they may also offer investors a broader allocation option beyond impact. Most green bonds are either government or corporate investment grade and issued widely in developed market, as well as certain emerging market countries. This potentially positions the portfolio well as an alternative, or compliment, to a global aggregate allocation.
Just like other fixed income asset classes, green bonds can be invested into in different investment styles. At a time of volatility, having flexibility to manage duration and move across credit quality and geographies may be helpful to seek the best opportunities. Green bonds are now able to offer investors this flexibility in approach. While a dynamic approach that invests in high yield and emerging markets may only be for investors with a higher risk appetite, the ability to invest across the duration curve may also be a useful tool for investors looking to reduce interest rate risk through short duration bonds. This means that investors may keep the benefit of green bonds while reducing their duration profile without necessarily giving up yield due to the characteristic of the universe and current yield curve inversion.
The growth of green bonds issuance allows investors greater scope for how they allocate to the asset class whether as an alternative, or a compliment, to a global aggregate or reflecting different styles and risk profiles within their portfolios.
References to companies and sector are for illustrative purposes only and should not be viewed as investment recommendations.

Green, Social and Sustainability Bonds Q&A Part Two: Social impact investing and beyond
We answer questions about social and sustainability bonds and how AXA IM helps power the transition to a sustainable economy.
Read the articleDisclaimer
This document is for informational purposes only and does not constitute investment research or financial analysis relating to transactions in financial instruments as per MIF Directive (2014/65/EU), nor does it constitute on the part of AXA Investment Managers or its affiliated companies an offer to buy or sell any investments, products or services, and should not be considered as solicitation or investment, legal or tax advice, a recommendation for an investment strategy or a personalized recommendation to buy or sell securities.
Due to its simplification, this document is partial and opinions, estimates and forecasts herein are subjective and subject to change without notice. There is no guarantee forecasts made will come to pass. Data, figures, declarations, analysis, predictions and other information in this document is provided based on our state of knowledge at the time of creation of this document. Whilst every care is taken, no representation or warranty (including liability towards third parties), express or implied, is made as to the accuracy, reliability or completeness of the information contained herein. Reliance upon information in this material is at the sole discretion of the recipient. This material does not contain sufficient information to support an investment decision.
Issued in the UK by AXA Investment Managers UK Limited, which is authorised and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority in the UK. Registered in England and Wales No: 01431068. Registered Office: 22 Bishopsgate London EC2N 4BQ
In other jurisdictions, this document is issued by AXA Investment Managers SA’s affiliates in those countries.
AXA IM and BNPP AM are progressively merging and streamlining our legal entities to create a unified structure
AXA Investment Managers joined BNP Paribas Group in July 2025. Following the merger of AXA Investment Managers Paris and BNP PARIBAS ASSET MANAGEMENT Europe and their respective holding companies on December 31, 2025, the combined company now operates under the BNP PARIBAS ASSET MANAGEMENT Europe name.